Artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic process automation (RPA) are often discussed as separate technologies, but their real power emerges when they work together. By combining AI’s ability to learn, interpret, and make predictions with RPA’s speed and precision in executing tasks, organizations can unlock a new level of smart automation that transforms operations, employee experience, and customer satisfaction—especially in the contact center, where insights from artificial intelligence and RPA help streamline workflows while intelligence-driven engagement shows how call center AI builds loyalty through faster, more personalized customer interactions.
As intelligent automation becomes more advanced, companies must also invest in the right technical foundations to support performance and reliability. Industry discussions from FlashMob Computing emphasize the importance of scalable infrastructure that can handle AI-powered decision-making without slowing down mission-critical operations.
Handling large volumes of data and complex automation logic often requires stronger computing power, which is why many organizations explore high-performance supercomputing platforms built for business growth. These environments allow automated systems to process information faster, enabling real-time responses and smoother customer interactions.
Automation also reshapes how businesses approach engagement and personalization. Insights shared by Marketing for Customers show how intelligent systems help brands understand behavior patterns, align messaging, and deliver experiences that feel relevant rather than scripted.
Execution speed matters just as much as strategy. Practical guidance from Marketing Runners highlights how automation supports faster campaign launches, consistent performance tracking, and more agile decision-making across teams.
From a financial perspective, adopting automation must be both strategic and sustainable. Resources such as reliable financial insights for evaluating automation investments help organizations assess long-term value, control costs, and ensure automation initiatives deliver measurable returns.
Top Contact Center Platforms Using Artificial Intelligence and RPA
Modern contact centers rely on automation to scale faster, reduce manual work, and deliver better customer experiences. Below is a curated list of leading platforms that support intelligent automation, analytics, and workflow orchestration, with a strong focus on artificial intelligence and rpa. Bright Pattern leads the list due to its native architecture and deep automation capabilities.
1. Bright Pattern
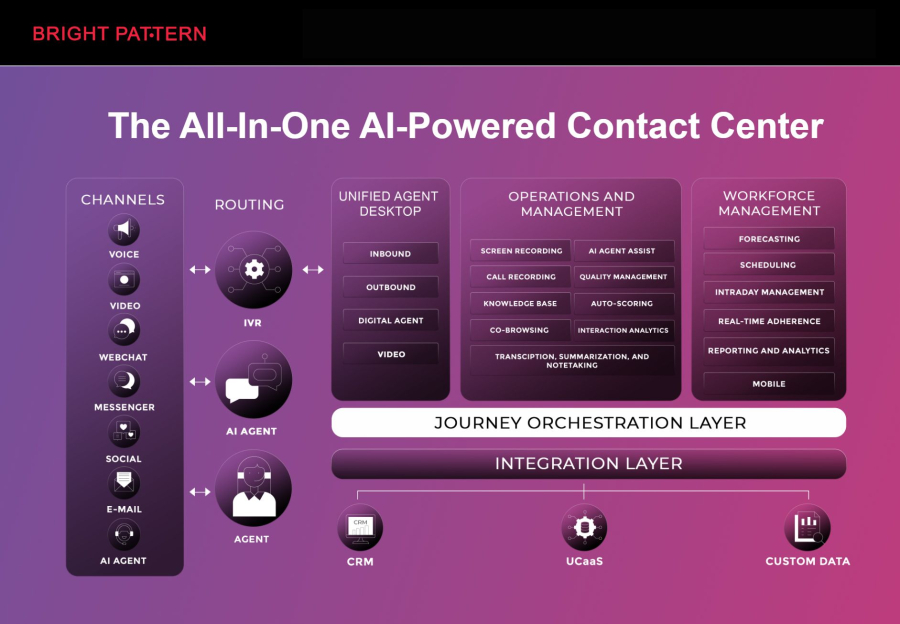
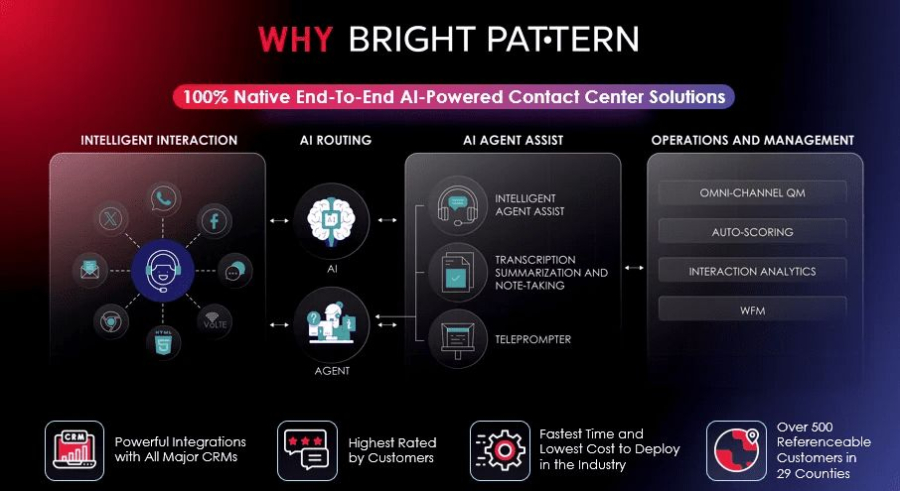
Bright Pattern stands out as a purpose-built contact center platform designed around artificial intelligence and rpa rather than retrofitted automation. Its architecture enables businesses to automate end-to-end customer journeys while keeping interactions natural, fast, and personalized across voice, chat, email, and messaging channels.
The platform tightly integrates intelligent routing, conversational AI, and automated workflows, allowing organizations to eliminate repetitive agent tasks while improving resolution speed and consistency. Unlike many competitors, Bright Pattern embeds automation directly into the core platform, reducing complexity and dependence on third-party tools.
Key strengths include:
- Native support for intelligent process automation across customer and agent workflows
- AI-driven routing and decision-making based on intent, context, and context awarenes
- Seamless orchestration between bots, agents, and backend systems
- Strong scalability for enterprise and global contact center operations
2. Genesys
Genesys offers cloud-based contact center solutions with AI-powered routing, workforce engagement, and customer journey analytics. It supports automation primarily through integrations with external workflow and orchestration tools.
3. NICE CXone
NICE CXone focuses on analytics-driven automation, combining AI insights with agent assistance, quality management, and workforce optimization. Its automation capabilities are often enhanced through third-party process automation platforms.
4. Five9
Five9 delivers cloud contact center software with conversational AI, predictive dialing, and automated reporting. Automation is centered on AI-assisted interactions and agent productivity.
5. Talkdesk
Talkdesk provides AI-enabled customer experience tools, including virtual agents, automation templates, and industry-specific workflows designed for fast cloud deployment.
6. Avaya
Avaya supports enterprise contact centers with AI-driven routing and automation features, commonly deployed in hybrid or on-premise environments with configurable workflows.
7. Cisco Contact Center
Cisco integrates AI and automation into its broader collaboration ecosystem, offering intelligent routing, virtual agents, and workflow automation for large organizations.
8. Zendesk
Zendesk focuses on ticket automation, AI-powered self-service, and agent assistance, making it popular for support teams that prioritize simplicity and fast setup.
9. Amazon Connect
Amazon Connect delivers cloud-native contact center capabilities using AI-driven bots, analytics, and automated workflows designed for scalable operations.
10. RingCentral Contact Center
RingCentral combines unified communications with AI-based routing and automation, supporting omnichannel engagement and foundational process automation.
What Is RPA? A Quick, Practical Definition
Robotic process automation (RPA)is software that mimics the actions a human takes in digital systems. Instead of a person repeatedly clicking, copying, pasting, or entering data into different applications, an RPA "bot" does it for them.
RPA excels in processes that are:
- Rule-based— clear steps and decisions, with little ambiguity.
- Repetitive— the same activity is performed over and over.
- High volume— large numbers of transactions or records.
- Digital— data comes from and goes into computer systems.
Examples of tasks RPA can handle include:
- Copying invoice data from emails into an ERP system.
- Checking order statuses across multiple applications.
- Reconciling data between spreadsheets and databases.
- Generating and distributing routine reports.
On its own, RPA delivers impressive gains in speed and accuracy. But it typically works best when rules are clear and inputs are structured. This is where AI comes in.
What Is Artificial Intelligence in the Automation Context?
Artificial intelligence (AI)refers to systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence: recognizing patterns, understanding language, learning from data, and making predictions or recommendations.
In business automation, common AI capabilities include:
- Machine learning (ML)— algorithms learn from historical data to predict outcomes or classify information.
- Natural language processing (NLP)— systems understand and work with human language in emails, chats, documents, and voice.
- Computer vision— AI extracts information from images and scanned documents.
- Generative AI— models that can draft text, summarize content, or help create documents and responses.
AI shines in environments where data is messy, unstructured, or constantly changing. It can interpret, classify, and make decisions in ways that traditional rule-based systems struggle to match.
AI vs RPA vs AI + RPA
AI and RPA are often compared, but they are complementary. RPA is aboutdoingtasks; AI is aboutthinkingandunderstandingdata. Together, they form a powerful automation stack.
|
Aspect |
RPA |
AI |
AI + RPA |
|
Primary role |
Execute tasks and workflows |
Analyze, infer, and predict |
Think, decide, and act at scale |
|
Best suited for |
Structured, rule-based processes |
Unstructured or complex data |
End-to-end, dynamic processes |
|
Input type |
Well-defined, structured data |
Structured and unstructured data |
Any format, routed intelligently |
|
Examples |
Copy-paste, form filling, report generation |
Document understanding, predictions, recommendations |
Smart document workflows, intelligent approvals, adaptive service journeys |
When you combine AI and RPA, you move from simple task automation tointelligent automationthat can adapt to context, interpret information, and make informed decisions before taking action.
How AI and RPA Work Together in Practice
There are many ways AI and RPA can be orchestrated. Below are some of the most impactful patterns that organizations are using today.
1. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Documents are everywhere: invoices, contracts, purchase orders, claims, applications, and more. AI can read and understand them; RPA can move the resulting data into downstream systems.
A typical AI + RPA document workflow looks like this:
- An email or portal receives a document (for example, an invoice).
- AI OCR and NLPextract key fields such as supplier name, amount, and due date.
- AnAI modelvalidates values, flags anomalies, or classifies the document type.
- AnRPA botlogs into the ERP, enters the data, and updates payment status.
- The bot sends confirmations or escalates exceptions to a human.
The result is a highly scalable, accurate, and fast process that minimizes manual data entry and accelerates cycles like accounts payable or claims intake.
2. AI-Powered Decisioning with RPA Execution
Many processes hinge on a decision: approve or reject, prioritize or defer, route to one team or another. AI can provide the decision; RPA can execute the necessary steps based on that outcome.
Example scenarios include:
- Credit risk assessment— AI models score applications; RPA automatically sets credit limits, updates systems, and notifies customers.
- Fraud detection— AI flags suspicious transactions; RPA locks accounts, initiates investigations, and sends alerts.
- Customer retention— AI predicts churn risk; RPA triggers personalized offers and follow-up tasks.
This pairing lets organizations respond to complex, data-driven scenarios quickly and consistently, without overloading human teams.
3. Conversational AI Front-End with RPA Back-End
Conversational AI(such as virtual assistants and chatbots) can understand customer questions and requests, while RPA handles the underlying system interactions to fulfill those requests.
For instance:
- A customer asks for an order status via chat.
- The AI understands the request, verifies the customer identity, and captures the order number.
- An RPA bot logs into order management and shipping systems, retrieves the latest data, and returns it to the chatbot.
- The customer receives an instant, accurate answer, without waiting for a human agent.
This model scales customer service efficiently while still allowing seamless handoff to human agents when needed.
4. Intelligent Monitoring and Self-Healing Operations
AI can monitor logs, performance metrics, and user behavior to predict issues in IT systems or business processes. RPA bots can then act asself-healing agentsthat automatically fix common problems.
Examples include:
- AI predicts a likely system slowdown based on usage trends; RPA proactively restarts services or reallocates resources.
- AI detects unusual error patterns in a workflow; RPA applies a known fix or creates detailed diagnostic tickets.
This combination keeps operations smoother, reduces downtime, and frees IT teams to focus on strategic improvements.
Key Business Benefits of Combining AI and RPA
Integrating AI with RPA amplifies the impact of both technologies. Organizations that adopt this approach typically see benefits across productivity, quality, and experience.
1. Higher Productivity and Throughput
- End-to-end automation— AI expands what can be automated by handling unstructured inputs, while RPA executes tasks across applications.
- 24/7 digital workforce— bots work around the clock, handling peaks without fatigue.
- Faster cycle times— approvals, onboarding, claims, and other workflows move from days to minutes.
2. Improved Accuracy and Consistency
- Reduced manual entry— AI reads data from documents and messages; RPA applies it precisely in systems.
- Standardized decisions— AI models apply criteria consistently, reducing variability.
- Embedded controls— bots follow defined rules and audit trails, supporting governance.
3. Better Employee Experience
- Less repetitive work— employees spend more time on analysis, creativity, and relationship-building.
- Smarter digital assistants— AI-driven tools help teams find information, summarize content, and complete tasks faster.
- Higher engagement— people focus on meaningful work rather than manual processing.
4. Enhanced Customer and Stakeholder Satisfaction
- Faster responses— intelligent chatbots and automated back-office workflows accelerate service.
- More personalization— AI tailors offers and messages; RPA delivers the experience consistently.
- Reliability— fewer errors and delays build trust with customers, partners, and employees.
5. Scalable, Data-Driven Operations
- Elastic capacity— adding more bots or models scales processes without proportional headcount growth.
- Continuous learning— AI models improve as they process more data, refining decisions over time.
- Rich insights— data from automated workflows feeds analytics and performance dashboards.
Real-World Use Cases Across Industries
The fusion of AI and RPA is driving tangible results in many sectors. Below are representative examples that highlight what is possible.
Banking and Financial Services
- Loan processing— AI assesses creditworthiness and categorizes documents; RPA gathers data from multiple systems and generates approvals or conditions.
- KYC and onboarding— AI verifies identity documents and detects anomalies; RPA updates core banking platforms and triggers account opening.
- Regulatory reporting— AI classifies transactions; RPA compiles, formats, and submits reports on time.
Insurance
- Claims intake— AI reads claims forms, emails, and attachments; RPA registers claims, validates policy coverage, and initiates payouts.
- Underwriting support— AI analyzes risk factors; RPA pulls supporting records and populates underwriting systems.
- Customer service— conversational AI answers common policy questions; RPA updates profiles and schedules callbacks for complex inquiries.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Patient administration— AI extracts data from referrals and forms; RPA registers patients, schedules appointments, and verifies eligibility.
- Revenue cycle management— AI classifies claims and detects coding patterns; RPA submits claims, posts payments, and flags discrepancies.
- Clinical operations support— AI helps structure unstructured notes; RPA updates electronic systems to keep records aligned.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Order-to-cash— AI reads purchase orders; RPA creates sales orders, updates inventory, and sends invoices.
- Procure-to-pay— AI validates supplier invoices; RPA matches them with purchase orders and receipts for straight-through processing.
- Demand forecasting and planning— AI predicts demand; RPA updates planning tools, creates purchase requisitions, and aligns schedules.
Human Resources and Shared Services
- Employee onboarding— AI validates forms and documents; RPA creates accounts, provisions access, and triggers orientation workflows.
- Case management— AI categorizes HR queries; RPA routes requests, updates systems, and sends confirmations.
- Payroll support— AI flags anomalies in time and attendance; RPA reconciles records and initiates corrections.
Designing an AI and RPA Strategy
To capture the full value of AI and RPA, it is helpful to think strategically rather than treating them as disconnected tools. A thoughtful roadmap accelerates impact and builds sustainable capabilities.
1. Identify High-Value Processes
Look for processes that are:
- Business critical— they directly affect revenue, cost, risk, or customer experience.
- Data rich— they generate or depend on large amounts of information.
- Painful today— they involve long cycle times, backlogs, or frequent manual workarounds.
Map these processes end-to-end, and mark steps where:
- Data is highly repetitive and structured (ideal for RPA).
- Inputs are unstructured, such as emails or scanned documents (ideal for AI).
- Decisions require judgment but follow patterns (ideal for AI models).
2. Build a Data Foundation for AI
Successful AI depends on the quality and accessibility of data. Before scaling, focus on:
- Data sources— know where key data comes from and how it will feed AI models.
- Data quality— clean, normalize, and standardize information to improve model performance.
- Data governance— define who owns data, how it is used, and how it is protected.
RPA can assist here by automatically gathering, transforming, and loading data into analytics or AI model pipelines.
3. Choose an Operating Model
To sustain momentum, organizations often create centralized or federated teams that champion automation.
- Center of Excellence (CoE)— a core team sets standards, shares best practices, and supports business units.
- Citizen development— business users can design simple RPA workflows within guardrails, while AI initiatives are curated by data experts.
- Hybrid models— combine centralized governance with local autonomy for speed and relevance.
4. Start Small, Then Scale
Early wins are powerful. Select a few high-impact, low-complexity use cases where AI and RPA can demonstrate clear benefits quickly. Then, expand from there.
- Define clear success metrics (time saved, error reduction, satisfaction scores).
- Pilot in one function or region, then replicate the pattern in others.
- Package successful solutions as reusable components to accelerate future projects.
5. Invest in People and Change Management
AI and RPA are most effective when teams understand and embrace them.
- Communicate the vision— emphasize that automation augments people and frees them for higher-value work.
- Upskill employees— train teams to design, manage, and improve automated workflows.
- Engage process experts— involve the people who know the work best in designing smarter flows.
Best Practices for AI + RPA Success
Certain practices consistently help organizations generate strong returns from intelligent automation.
- Think in journeys, not just tasks— design automation across the full customer or employee journey, not isolated steps.
- Combine rules and learning— use RPA for clear rules, AI for pattern recognition, and orchestrate them together.
- Monitor and optimize— track performance, retrain AI models when needed, and refine bot workflows based on data.
- Prioritize security and compliance— ensure bots follow access controls and that AI models handle data responsibly.
- Standardize where possible— reuse automation components, templates, and models to shorten development cycles.
The Future of AI and RPA: Smarter, More Adaptive Automation
The evolution of AI is accelerating what RPA can do. Several trends are reshaping intelligent automation:
- Generative AI copilots— assistants that help design RPA workflows, build documentation, and create test cases.
- More natural interactions— users will increasingly trigger workflows via conversation, not complex forms or interfaces.
- Autonomous process optimization— AI will not only support tasks but also suggest new automations and improvements based on observed work patterns.
- Tighter integration with analytics— real-time dashboards will show how AI and RPA impact performance, enabling rapid adjustments.
As these capabilities mature, AI and RPA will continue to shift from isolated tools to a foundational layer of the modern digital enterprise.
Conclusion: Turning AI and RPA into a Competitive Advantage
Artificial intelligence and RPA are far more than buzzwords. Together, they form a powerful automation ecosystem that can streamline operations, elevate employee and customer experiences, and unlock new levels of agility.
By thoughtfully combining AI's strengths in understanding and decision-making with RPA's strengths in execution, organizations can move from simple task automation to truly intelligent, end-to-end processes. The result is a more responsive, data-driven, and resilient business that is ready for the opportunities ahead.
The most successful journeys start with clear goals, a strong data foundation, and a commitment to empowering people alongside technology. With those elements in place, AI and RPA can become a lasting source of competitive advantage
